What am I going to learn in Geography?
Year 1 – Spatial Sense
The word aerial means from above. When we look at something from above, we call this an ‘aerial view’. Sometimes objects look different from an aerial view.
Maps give us information about places. Location means where something is. Maps use symbols to show where things are.
Location means the place where something is. We can use words to describe location. We can use words to compare the location of different places.
We can give directions such as forwards, backwards, left or right. Compasses can be used to find direction and navigate. A compass has four points; north, south, east and west.
Maps often have a title, labels and symbols. Maps often have a key which explains any symbols. Maps often have a compass showing north, south, east and west.

Year 2 – Spatial Sense – Maps and Globes
Maps show us information about different places. ‘Site’ means where something, like a building, is located. (Insert locally relevant detail) are located on the site of my school.
People who draw maps are called cartographers. Maps must be clear and easy to read. Maps may include labels and symbols that give us more information.
Maps use symbols to tell us information about the local area. We can use maps to describe location and to navigate. An Ordnance Survey map can help us find human and physical features of an area.
We can use a map to plan a route. Routes need a starting point and a destination. Compass directions help us know which direction to travel in.
A globe is a model of the Earth. World maps and globes show us the continents and the oceans. The Equator is an imaginary line halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole.
![]()

Year 3 – Spatial Sense
A map shows information about an area of land. (Securing prior knowledge) The eight points of a compass are: north, north-east, east, south-east, south, south-west, west and north-west. Compasses use magnetism to show direction.
Maps were made long ago to help the army fight invasions. Ordnance Survey is an organisation that produces maps of the UK. Maps use symbols to show us information about locations.
Grid references tell us where to find a place on a map. The grid references are usually labelled as either numbers or letters. The horizontal lines are referred to as ‘northings’, whereas the vertical lines are called ‘eastings’.
Physical geography refers to natural features of the earth. We can compare the physical features of different places by looking at maps and photographs. We can identify the main differences between the two landscapes.
Human geography refers to features of the environment made by people. We can compare the human features of different places by looking at maps, photographs and other information. We can identify the similarities and differences between London and San Francisco.

Year 4 – Spatial Sense
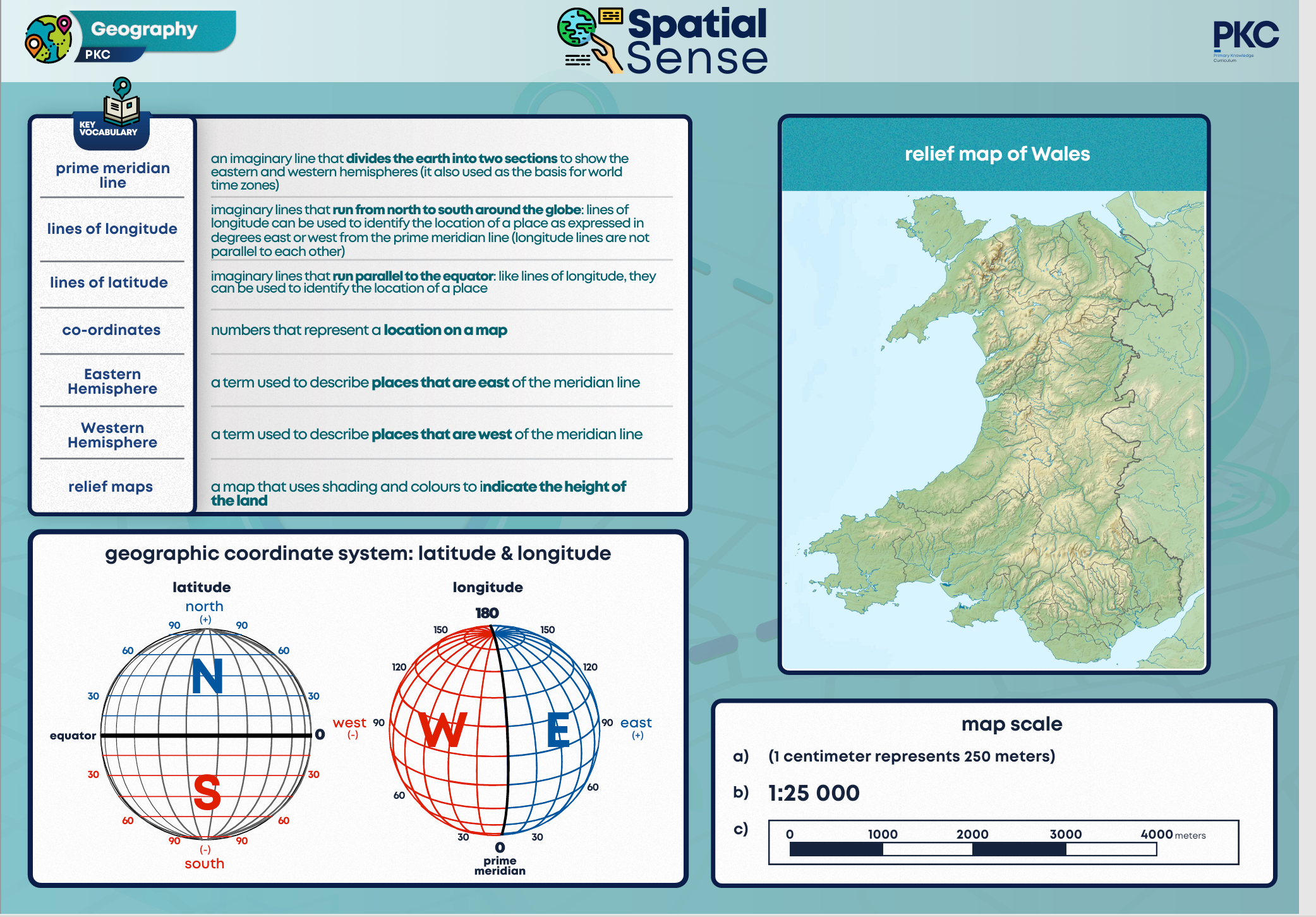
Latitude lines run parallel to the equator and tell us how far north or south a location is. Longitude lines parallel to the Prime Meridian line and tell us how far east or west a location is. The Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn are areas where the sun can be directly overhead.
Scale tells us the distance between places on a map. Some maps show an area in large scale with lots of detail. Some maps show an area in small-scale with very little detail.
Grid references have information that help us to find locations. The horizontal lines are called ‘northings’. The vertical lines are called ‘eastings’.
![]()

Year 5 – Spatial Sense
Cartographers use imaginary lines to help them locate places on maps. Lines of latitude are parallel to the equator, running from east to west. Lines of longitude run from the poles; from north to south.
There are four hemispheres; northern, southern, eastern and western. The Prime Meridian divides the Eastern and Western hemispheres. The Prime Meridian runs through Greenwich in London.
Co-ordinates can be used to help us locate places on a map. A co-ordinate is a point where lines on a globe cross over. When we write coordinates, we write the latitude first, then the longitude.
Maps are drawn to different scales; some show us small areas, others show us large areas. Map scale is the proportion between the distance on a map and the actual distance on the earth’s surface. A map scale helps us to measure distance between places on a map.
A relief map is a kind of map that shows how high land is. On relief maps, colours can be used to show heights; dark green means at the same height as the sea, through yellow to brown. For smaller areas, contours can be used to show how the land height is changing.
Year 6 – Spatial Sense
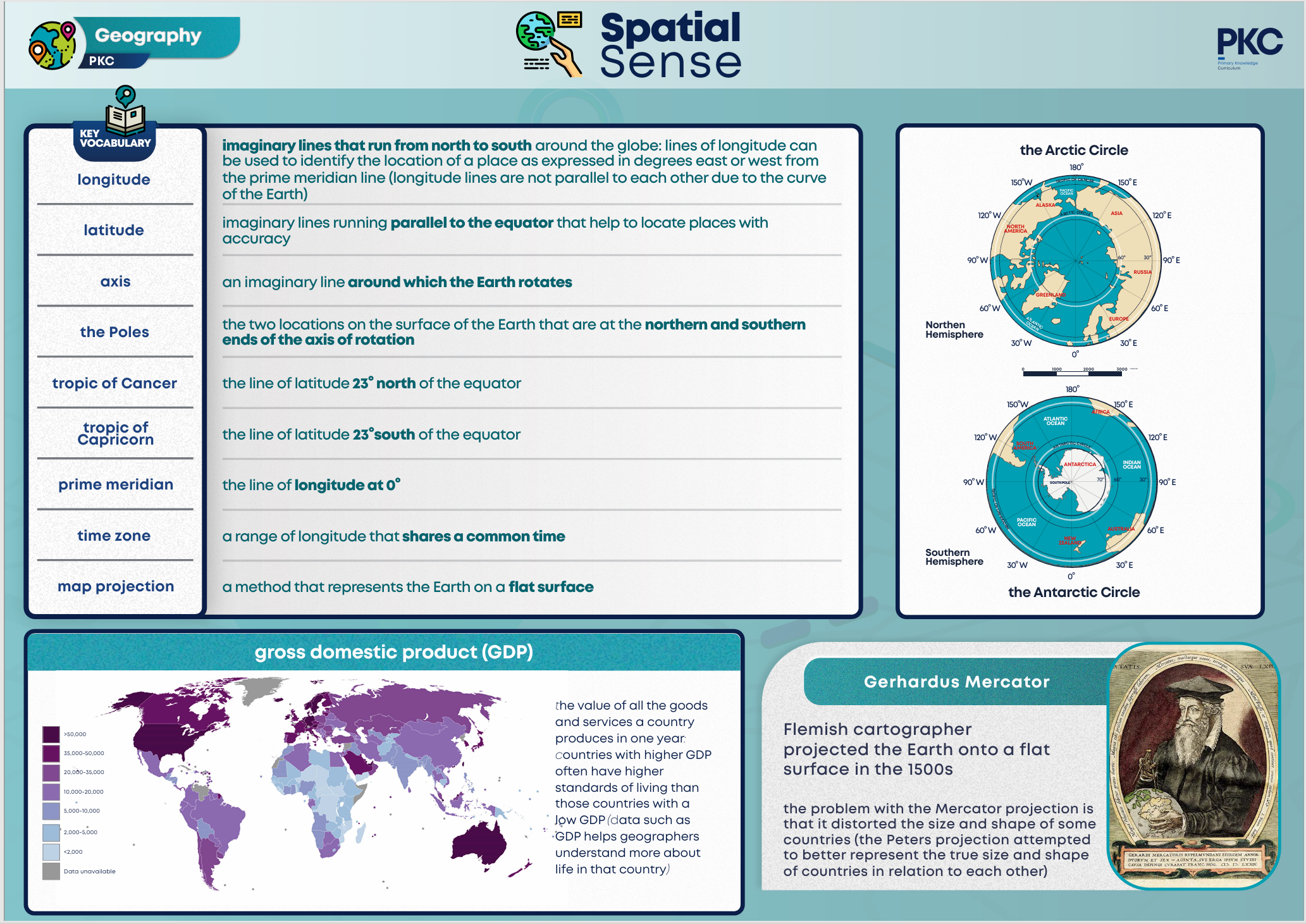
Lines of longitude run from the North Pole to the South Pole. Lines of latitude run parallel to the equator. The points where lines of longitude and latitude intersect are coordinates.
The Arctic Circle is a region around the North Pole. The Antarctic Circle is a region around the South Pole. In the Arctic and Antarctic Circles there are winter days when the sun doesn’t rise, and summer days when the sun doesn’t set. Polar Night and Midnight Sun are caused by the tilt of the earth on its axis.
The Prime Meridian is the point where the world begins to be divided into 24 sections called time zones. Within a time zone, people observe the same time as it is convenient for business, trade and communications. Some countries adjust their clocks for daylight saving time.
Cartographers have tried different ways to represent our round earth on a flat map. The Mercator projection has been used for a long time, but land near the poles appears larger than it should. The Peters projection tries to show the correct size of countries in relation to each other.
Maps can help us to understand data about people, places and the environment. Wealth distribution around the world is uneven. (Change as appropriate to the maps you are using) Food consumption around the world is uneven.
![]()
